Gene Krupa was born in Chicago, Illinois on January
15, 1909 and was the the youngest of Bartley and Ann Krupa's nine
children. His father died when Gene was very young and his mother worked
as a milliner to support the family. All of the children had to start
working while young, Gene at age eleven. His brother Pete worked at
"Brown Music Company", and got Gene a job as chore boy. Gene started out
playing sax in grade school but took up drums at age 11 since they were
the cheapest item in the music store where he and his brother worked. "I
used to look in their wholesale catalog for a musical instrument -
piano, trombone, cornet - I didn't care what it was as long as it was an
instrument. The cheapest item was the drums, 16 beans, I think, for a
set of Japanese drums; a great high, wide bass drum, with a brass cymbal
on it, a wood block and a snare drum."
His parents were very religious
and had groomed Gene for the priesthood. He spent his grammar school
days at various parochial schools and upon graduation went to St.
Joseph's College for a brief year. Gene's drive to drum was too strong
and he gave up the idea of becoming a priest. In 1921, while still in
grammar school, Gene joined his first band "The Frivolians." He obtained
the drumming seat as a fluke when the regular drummer was sick. The band
played during summers in Madison, Wisconsin. Upon entering high school
in 1923, Gene became buddies with the "Austin High Gang", which included
many musicians which would be on Gene's first recording session; Jimmy McPartland, Jimmy Lanigan, Bud Freeman and Frank Teschemacher. In 1925, Gene began his
percussion studies with Roy Knapp, Al Silverman & Ed Straight. Under
advice from others, he decided to join the musicians union. "The guy
said, 'Make a roll. That's it. Give us 50 bucks. You're In.'" Krupa
started his first "legit" playing with Joe Kayser, Thelma Terry and the Benson Orchestra among other
commercial bands. A popular hangout for musicians was "The Three
Deuces." All of the guys playing in mickey mouse bands would gravitate
here after hours and jam till early in the morning. Gene was able to
hone and develop his style playing with other jazz players such as Mezz Mezzrow, Tommy Dorsey, Bix Beiderbecke and Benny Goodman in these local
dives. Krupa's big influences during this time were Tubby Hall and Zutty Singleton. The drummer who probably had the
greatest influence on Gene in this period was the great Baby Dodds. Dodds' use of press rolls was highly
reflected in Gene's playing, especially during his tenure with Benny
Goodman.
went to St.
Joseph's College for a brief year. Gene's drive to drum was too strong
and he gave up the idea of becoming a priest. In 1921, while still in
grammar school, Gene joined his first band "The Frivolians." He obtained
the drumming seat as a fluke when the regular drummer was sick. The band
played during summers in Madison, Wisconsin. Upon entering high school
in 1923, Gene became buddies with the "Austin High Gang", which included
many musicians which would be on Gene's first recording session; Jimmy McPartland, Jimmy Lanigan, Bud Freeman and Frank Teschemacher. In 1925, Gene began his
percussion studies with Roy Knapp, Al Silverman & Ed Straight. Under
advice from others, he decided to join the musicians union. "The guy
said, 'Make a roll. That's it. Give us 50 bucks. You're In.'" Krupa
started his first "legit" playing with Joe Kayser, Thelma Terry and the Benson Orchestra among other
commercial bands. A popular hangout for musicians was "The Three
Deuces." All of the guys playing in mickey mouse bands would gravitate
here after hours and jam till early in the morning. Gene was able to
hone and develop his style playing with other jazz players such as Mezz Mezzrow, Tommy Dorsey, Bix Beiderbecke and Benny Goodman in these local
dives. Krupa's big influences during this time were Tubby Hall and Zutty Singleton. The drummer who probably had the
greatest influence on Gene in this period was the great Baby Dodds. Dodds' use of press rolls was highly
reflected in Gene's playing, especially during his tenure with Benny
Goodman.
 Gene has often been considered to
be the first drum "soloist." Drummers usually had been strictly
time-keepers or noisemakers, but Krupa interacted with the other
musicians and introduced the extended drum solo into jazz. His goal was
to support the
Gene has often been considered to
be the first drum "soloist." Drummers usually had been strictly
time-keepers or noisemakers, but Krupa interacted with the other
musicians and introduced the extended drum solo into jazz. His goal was
to support the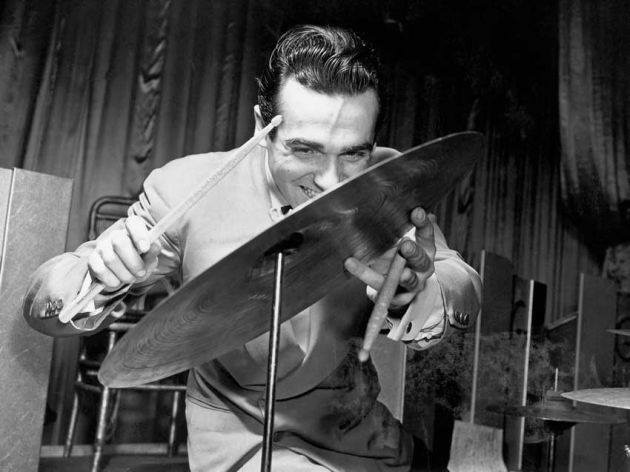 other musicians while creating his own role within
the group. Gene is also considered the father of the modern drumset
since he convinced H.H. Slingerland, of Slingerland Drums, to make tuneable tom-toms.
Tom-toms up to that point had "tacked" heads, which left little ability
to change the sound. The new drum design was introduced in 1936 and was
termed "Separate Tension Tunable
Tom-Toms." Gene was a loyal endorser of Slingerland Drums
from 1936 until his death. Krupa was called on by Avedis Zildjian to help with developing the modern
hi-hat cymbals. The original hi-hat was called a "low-boy" which was a
floor level cymbal setup which was played with the foot. This
arrangement made it nearly impossible for stick playing. Gene's first
recording session was a historical one. It occurred in December of 1927
when he is often credited to be the first drummer to record with a bass
drum (Baby Dodds had actually recorded with a bass drum prior to Gene).
Krupa, along with rest of the McKenzie-Condon Chicagoans were scheduled
to record at OKeh Records in Chicago. OKeh's Tommy Rockwell was
apprehensive to record Gene's drums but gave in. Rockwell said "All
right, but I'm afraid the bass drum and those tom-toms will knock the
needle off the wax and into the street."
other musicians while creating his own role within
the group. Gene is also considered the father of the modern drumset
since he convinced H.H. Slingerland, of Slingerland Drums, to make tuneable tom-toms.
Tom-toms up to that point had "tacked" heads, which left little ability
to change the sound. The new drum design was introduced in 1936 and was
termed "Separate Tension Tunable
Tom-Toms." Gene was a loyal endorser of Slingerland Drums
from 1936 until his death. Krupa was called on by Avedis Zildjian to help with developing the modern
hi-hat cymbals. The original hi-hat was called a "low-boy" which was a
floor level cymbal setup which was played with the foot. This
arrangement made it nearly impossible for stick playing. Gene's first
recording session was a historical one. It occurred in December of 1927
when he is often credited to be the first drummer to record with a bass
drum (Baby Dodds had actually recorded with a bass drum prior to Gene).
Krupa, along with rest of the McKenzie-Condon Chicagoans were scheduled
to record at OKeh Records in Chicago. OKeh's Tommy Rockwell was
apprehensive to record Gene's drums but gave in. Rockwell said "All
right, but I'm afraid the bass drum and those tom-toms will knock the
needle off the wax and into the street."
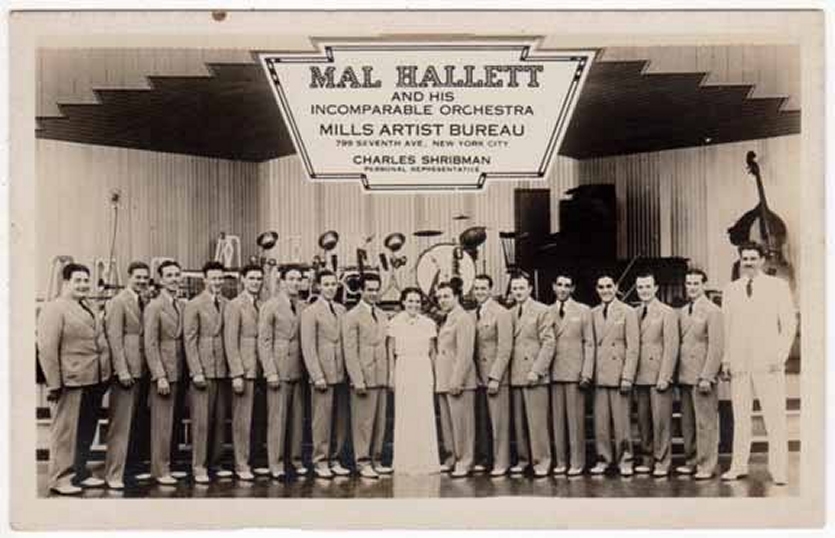 With Mal Hallett's Orchestra, 1933
With Mal Hallett's Orchestra, 1933
Gene moved to New York in 1929 and
was recruited by Red Nichols. He, along with Benny Goodman and Glenn Miller, performed in the pit band of the new
George
Gershwin play "Strike Up the Band." Gene had never learned to read
music and "faked" his parts during rehearsals. Glenn Miller assisted him
by humming the drum parts until Gene got them down. After "Strike Up the
Band" completed in January 1930, Hoagy Carmichael gathered several great musicians
together for many historical sessions. Gene played on some legendary
"jazz" recordings with Bix Beiderbecke, Adrian Rollini and Joe Venuti.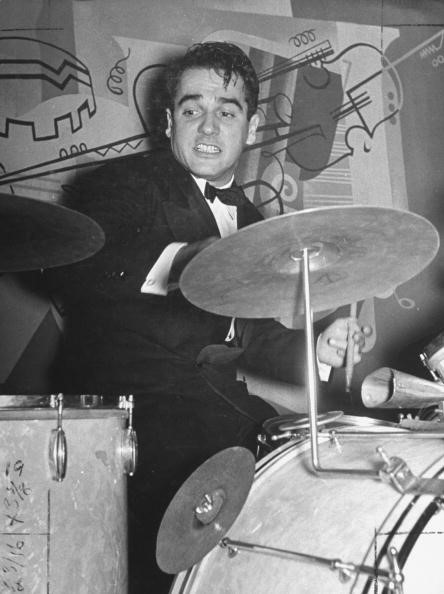 Krupa played in
one more pit band with Red Nichols for Gershwin's "Girl Crazy." He then
joined Russ Columbo's band in which indirectly led to his
joining Benny Goodman's group. Benny Goodman urged Gene to join his band
with the promise that it would be a real jazz band. After joining, Benny
soon became discouraged with the idea of having a successful jazz group.
The band was relegated to playing dance music and Benny was considering
packing it in. Upon the band's engagement at the Palomar, Benny decided
to go for broke and play their own arrangements. The audience went wild
and the band took off. The Goodman group featured Gene prominently in
the full orchestra and with the groundbreaking Goodman Trio and Quartet.
The Trio is possibly the first working small group which featured black
and white musicians. On January 16, 1938, the band was the first "jazz"
act to play New York's Carnegie Hall. Gene's classic performance on
"Sing Sing Sing" has been heralded as the first extended drum solo in
jazz. After the Carnegie
Hall performance, tension began to surface between Gene and Benny.
Audiences were demanding that Gene be featured in every number and Benny
didn't want to lose the spotlight to a sideman.
Krupa played in
one more pit band with Red Nichols for Gershwin's "Girl Crazy." He then
joined Russ Columbo's band in which indirectly led to his
joining Benny Goodman's group. Benny Goodman urged Gene to join his band
with the promise that it would be a real jazz band. After joining, Benny
soon became discouraged with the idea of having a successful jazz group.
The band was relegated to playing dance music and Benny was considering
packing it in. Upon the band's engagement at the Palomar, Benny decided
to go for broke and play their own arrangements. The audience went wild
and the band took off. The Goodman group featured Gene prominently in
the full orchestra and with the groundbreaking Goodman Trio and Quartet.
The Trio is possibly the first working small group which featured black
and white musicians. On January 16, 1938, the band was the first "jazz"
act to play New York's Carnegie Hall. Gene's classic performance on
"Sing Sing Sing" has been heralded as the first extended drum solo in
jazz. After the Carnegie
Hall performance, tension began to surface between Gene and Benny.
Audiences were demanding that Gene be featured in every number and Benny
didn't want to lose the spotlight to a sideman.
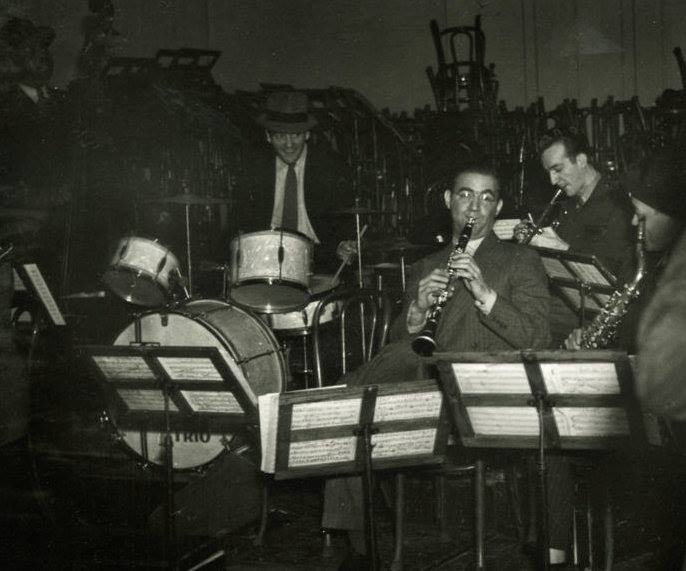 Rehearsing at Carnegie Hall with Benny
Goodman
Rehearsing at Carnegie Hall with Benny
Goodman
Gene departed on March 3, 1938 and
less than 2 months later formed his own orchestra. His band was an
instant success upon it's opening at the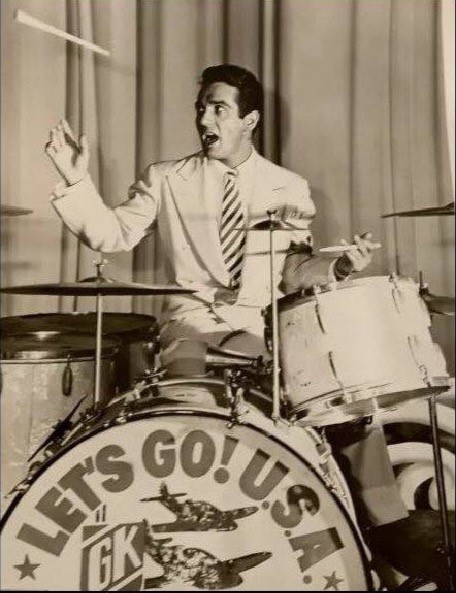 Marine Ballroom on the Steel
Pier in Atlantic City during April of 1938. His band went through
several incarnations during it's existance and at one point even
featured a string section with 30 to 40 members. During this time Krupa
authored his own book titled "The Gene Krupa Drum Method"(1938) and
began an annual Drum Contest(1941). The contest attracted thousands of
contestants each year and saw drum legend Louie Bellson as the first
year's winner. Gene appeared in several motion pictures including "Some
Like it Hot" & "Beat the Band", becoming a sort of matinee idol. His
noted likeness to Tyrone Power and musical fame was a magical
combination in the eyes of Hollywood. In the summer of 1943, Krupa was
arrested in San Francisco in a bogus drug bust. He was charged with
possession of marijuana and contributing to the delinquency of a
minor. In truth, the entire incident was a setup by a power-hungry
D.A. Gene was sentenced to 90 days, of which 84 were served. He
was later cleared of the latter charges. During this time, Roy Eldridge led Gene's band and eventually had to
break up the group. After Gene got out of jail, he briefly joined up
with Benny Goodman and Tommy Dorsey before re-forming his own band.
Krupa's groups of the early 1940's were often criticized as being too
commercial but Gene's big band was one of the first in the mid-forties
to introduce Bop arrangements with the help of Gerry Mulligan and the playing of trumpeter Red Rodney. Gene managed to keep the full band
together until December of 1950, when most big bands had already fallen
apart. He kept a smaller version of the big band together through 1951.
Read a detailed accounting of Gene's Drug
Arrest.
Marine Ballroom on the Steel
Pier in Atlantic City during April of 1938. His band went through
several incarnations during it's existance and at one point even
featured a string section with 30 to 40 members. During this time Krupa
authored his own book titled "The Gene Krupa Drum Method"(1938) and
began an annual Drum Contest(1941). The contest attracted thousands of
contestants each year and saw drum legend Louie Bellson as the first
year's winner. Gene appeared in several motion pictures including "Some
Like it Hot" & "Beat the Band", becoming a sort of matinee idol. His
noted likeness to Tyrone Power and musical fame was a magical
combination in the eyes of Hollywood. In the summer of 1943, Krupa was
arrested in San Francisco in a bogus drug bust. He was charged with
possession of marijuana and contributing to the delinquency of a
minor. In truth, the entire incident was a setup by a power-hungry
D.A. Gene was sentenced to 90 days, of which 84 were served. He
was later cleared of the latter charges. During this time, Roy Eldridge led Gene's band and eventually had to
break up the group. After Gene got out of jail, he briefly joined up
with Benny Goodman and Tommy Dorsey before re-forming his own band.
Krupa's groups of the early 1940's were often criticized as being too
commercial but Gene's big band was one of the first in the mid-forties
to introduce Bop arrangements with the help of Gerry Mulligan and the playing of trumpeter Red Rodney. Gene managed to keep the full band
together until December of 1950, when most big bands had already fallen
apart. He kept a smaller version of the big band together through 1951.
Read a detailed accounting of Gene's Drug
Arrest.
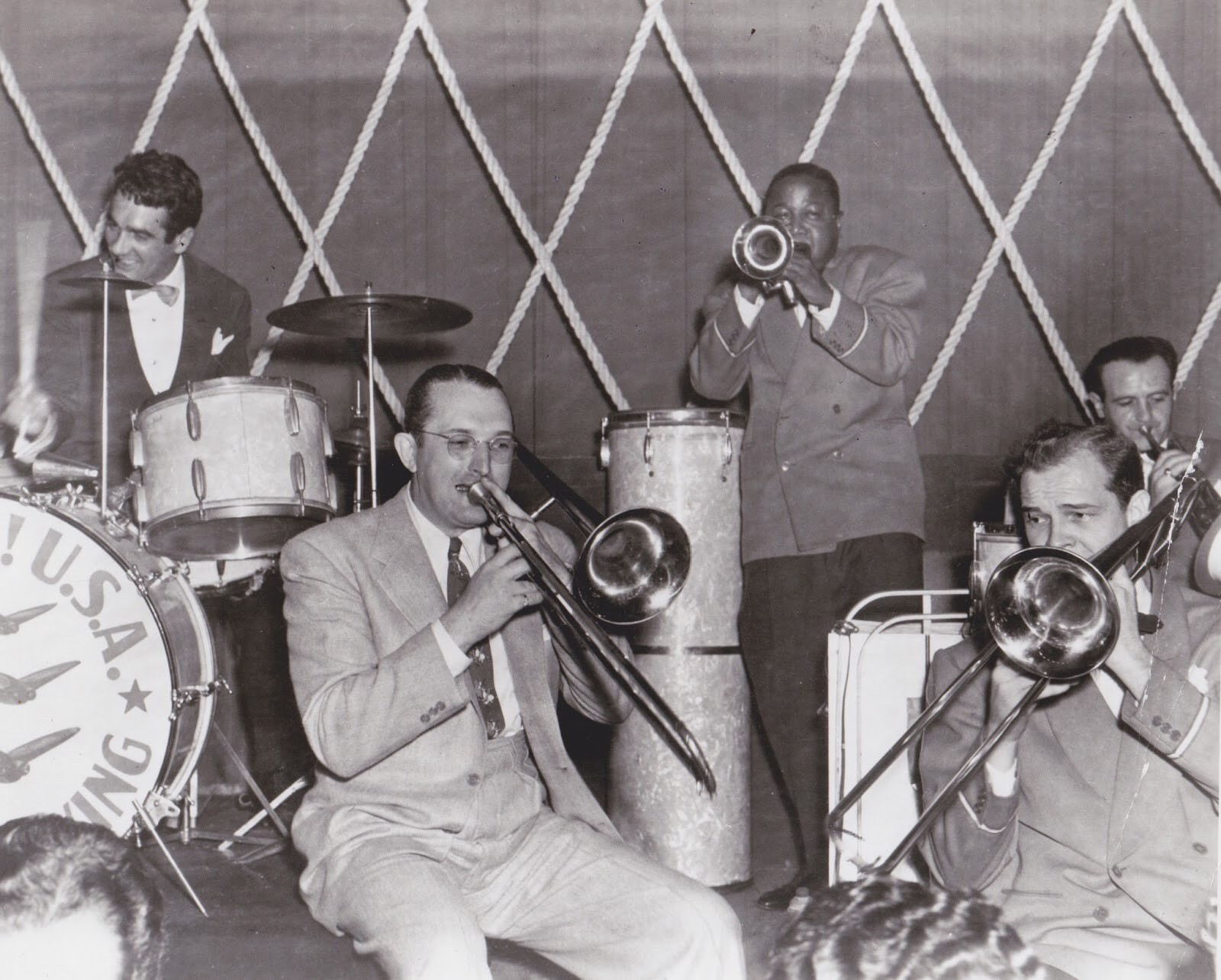 With Tommy Dorsey & Roy
Eldridge.
After breaking up his big band,
Gene wasn't sure which direction to take. He had led small groups within
his big band during the 40's, this was a logical choice with the growing
popularity of be-bop. The Gene Krupa Trio was one of the first acts
recruited by Norman Granz for his "Jazz At The Philharmonic"
concerts(due to contractual reasons, Gene was first billed as "The
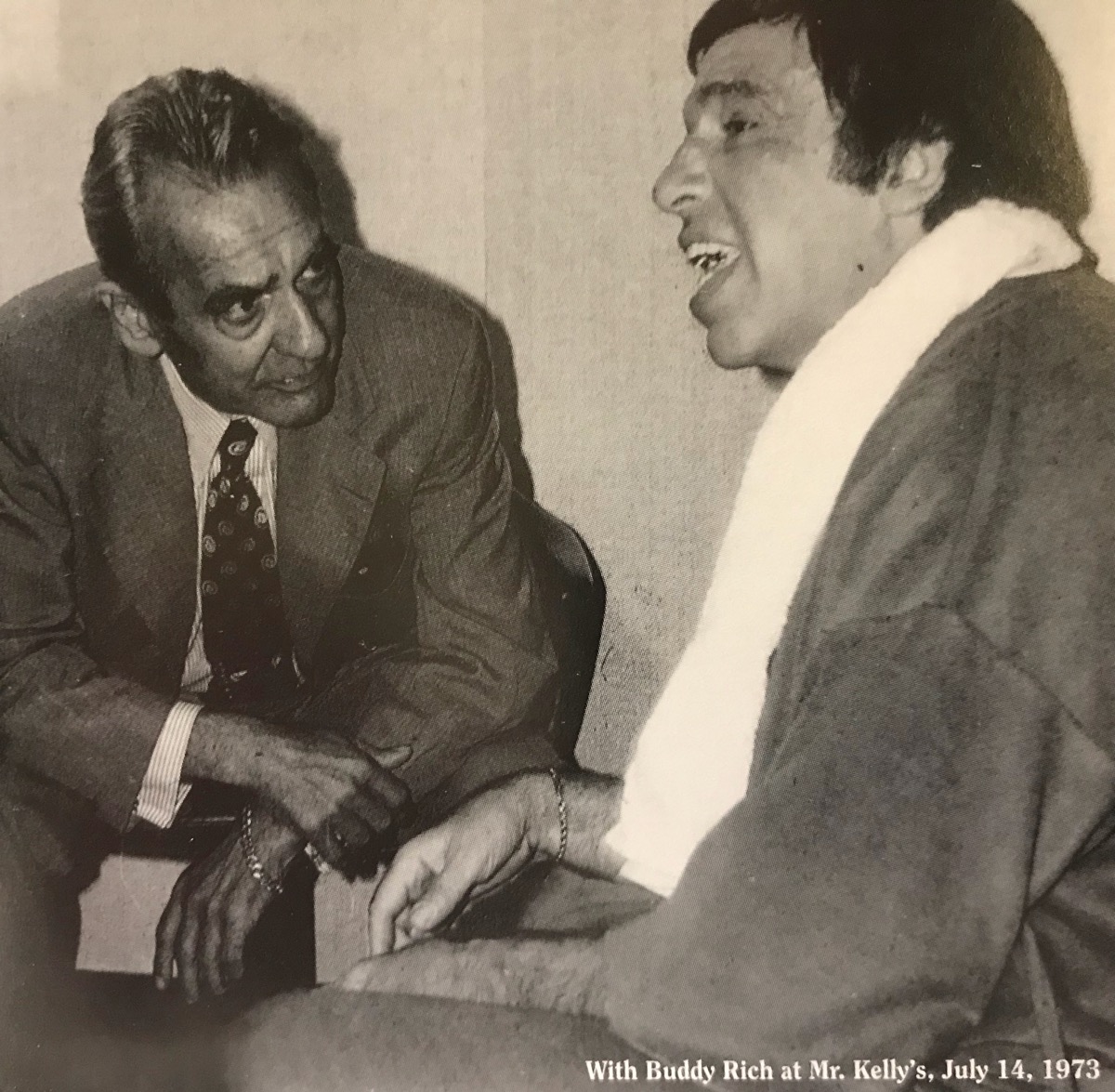
Chicago Flash."). The JATP dates introduced the famous "Drum Battles"
with Buddy Rich in October of 1952 and the subsequent studio recordings
on the Lp "Krupa and Rich" in 1955. Some of the greatest jazz recordings
of all time were the result of the "All-Star" jams at JATP. The alumni
of these dates included Lester
Young, Dizzy Gillespie, Charlie Shavers, Ray Brown, Lionel Hampton, Buddy Rich and of course, Gene. Along with Cozy Cole, Gene formed the Krupa-Cole Drum School
in March of 1954. He also began studying tympani with the New York
Philharmonic's Saul Goodman(1951). In 1959, actor Sal Mineo portrayed Gene in the motion picture
"The Gene Krupa Story." The film was very loose in the facts of Gene's
career but did feature an excellent soundtrack recorded by Krupa
himself. Gene's huge resurgence in popularity eventually led to his
departing the teaching role he had at the Drum School.
With Tommy Dorsey & Roy
Eldridge.
After breaking up his big band,
Gene wasn't sure which direction to take. He had led small groups within
his big band during the 40's, this was a logical choice with the growing
popularity of be-bop. The Gene Krupa Trio was one of the first acts
recruited by Norman Granz for his "Jazz At The Philharmonic"
concerts(due to contractual reasons, Gene was first billed as "The
Chicago Flash."). The JATP dates introduced the famous "Drum Battles"
with Buddy Rich in October of 1952 and the subsequent studio recordings
on the Lp "Krupa and Rich" in 1955. Some of the greatest jazz recordings
of all time were the result of the "All-Star" jams at JATP. The alumni
of these dates included Lester
Young, Dizzy Gillespie, Charlie Shavers, Ray Brown, Lionel Hampton, Buddy Rich and of course, Gene. Along with Cozy Cole, Gene formed the Krupa-Cole Drum School
in March of 1954. He also began studying tympani with the New York
Philharmonic's Saul Goodman(1951). In 1959, actor Sal Mineo portrayed Gene in the motion picture
"The Gene Krupa Story." The film was very loose in the facts of Gene's
career but did feature an excellent soundtrack recorded by Krupa
himself. Gene's huge resurgence in popularity eventually led to his
departing the teaching role he had at the Drum School.
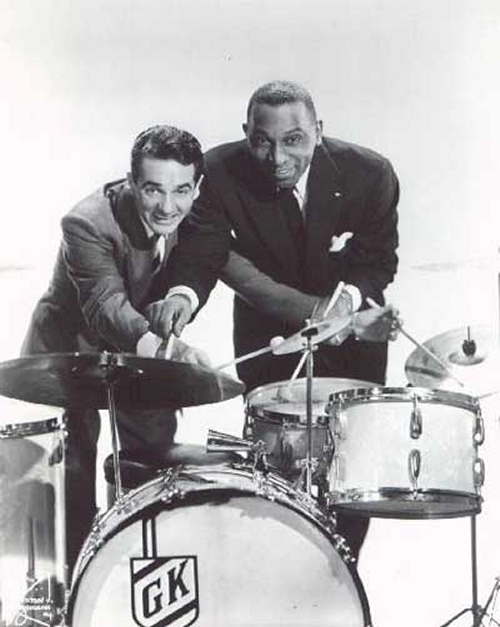

By
the late fifties Krupa was prompted to slow down due to increasing back
problems. He had a heart attack in 1960 which forced him into a
retirement for many months. After recuperating, the ever-changing
Quartet continued to perform, record and regularly appeared at New
York's Metropole. The Goodman Quartet reunited and played several live
dates. Gene led a hectic schedule with the Quartet through the early and
mid-sixties, performing throughout the US and abroad. His health once
again became a problem and his second marriage fell apart. He retired in
1967 proclaiming that "I feel too lousy to play and I know I must sound
lousy." During his hiatus, Krupa practiced and coached his baseball
team. In 1969, Gene began a series of anti-drug lectures and clinics for
Slingerland Drums. He officially came out of retirement in the spring of
1970, re-formed the Quartet and was featured at Hotel Plaza in New York.
Gene's last commercial recording was in November of 1972, titled "Jazz
At the New School" with Eddie Condon and Wild Bill Davison. Gene's final
public performance was with a reunion of the old Goodman Quartet on
August 18, 1973. His soloing ability was greatly diminished but his
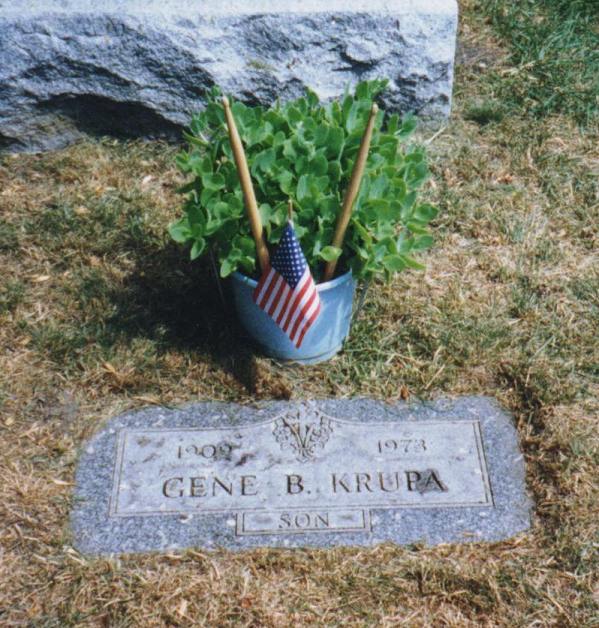
overall playing had become more modern sounding than ever. Gene died
October 16, 1973 of a heart attack. He had also been plagued by leukemia
and emphysema. He was laid to rest at the Holy Cross Cemetery in Calumet
City, Illinois.
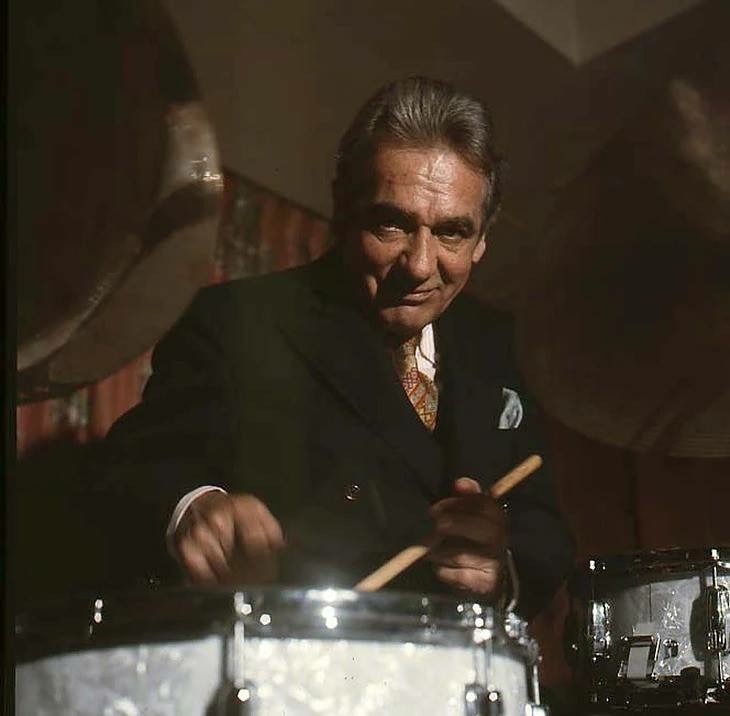
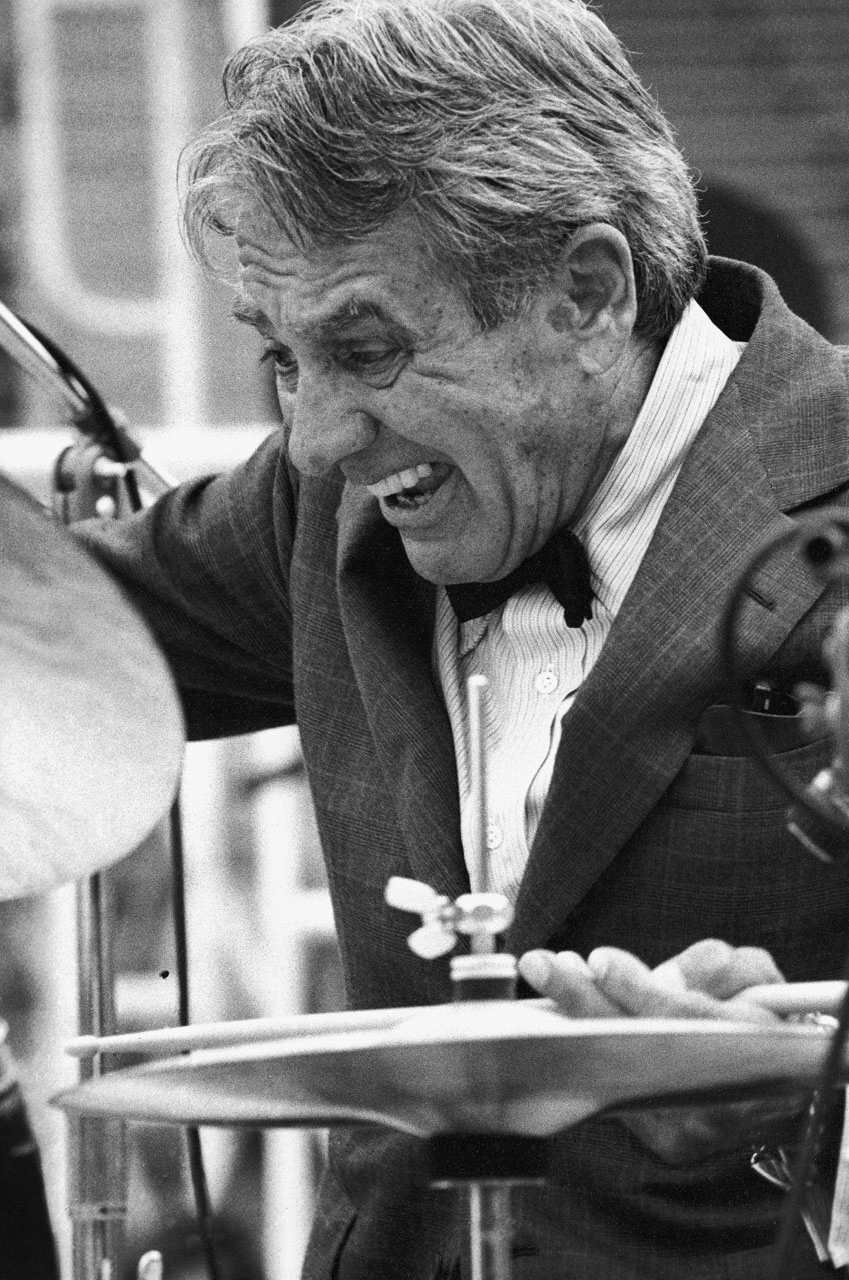

 Gene Krupa will forever be known
as the man who made drums a solo instrument. He single-handedly made the
Slingerland Drum Company a success and inspired millions to become
drummers. He also demonstrated a level of showmanship which has not been
equaled. Buddy Rich once said that Gene was the "beginning and the end
of all jazz drummers." Louie Bellson said of Gene, "He was a wonderful,
kind man and a great player. He brought drums to the foreground. He is
still a household name."
Gene Krupa will forever be known
as the man who made drums a solo instrument. He single-handedly made the
Slingerland Drum Company a success and inspired millions to become
drummers. He also demonstrated a level of showmanship which has not been
equaled. Buddy Rich once said that Gene was the "beginning and the end
of all jazz drummers." Louie Bellson said of Gene, "He was a wonderful,
kind man and a great player. He brought drums to the foreground. He is
still a household name."


(Biography) (Photo Gallery) ( Discography )
(Filmography)
(Gene Krupa/Buddy
Rich Interview)
(GK on Facebook) (Audio/Video ) (Jazz
Legends)
(Drug Bust)
(Drum & Cymbal
Setups) (Recollections)
(78 Labels)
(Modern Drummer
Tribute)
(Credits)
(Links)
(Home)
Copyright © 1997-2020, Shawn C. Martin.




 went to St.
Joseph's College for a brief year. Gene's drive to drum was too strong
and he gave up the idea of becoming a priest. In 1921, while still in
grammar school, Gene joined his first band "The Frivolians." He obtained
the drumming seat as a fluke when the regular drummer was sick. The band
played during summers in Madison, Wisconsin. Upon entering high school
in 1923, Gene became buddies with the "Austin High Gang", which included
many musicians which would be on Gene's first recording session; Jimmy McPartland, Jimmy Lanigan, Bud Freeman and Frank Teschemacher. In 1925, Gene began his
percussion studies with Roy Knapp, Al Silverman & Ed Straight. Under
advice from others, he decided to join the musicians union. "The guy
said, 'Make a roll. That's it. Give us 50 bucks. You're In.'" Krupa
started his first "legit" playing with Joe Kayser, Thelma Terry and the Benson Orchestra among other
commercial bands. A popular hangout for musicians was "The Three
Deuces." All of the guys playing in mickey mouse bands would gravitate
here after hours and jam till early in the morning. Gene was able to
hone and develop his style playing with other jazz players such as Mezz Mezzrow, Tommy Dorsey, Bix Beiderbecke and Benny Goodman in these local
dives. Krupa's big influences during this time were Tubby Hall and Zutty Singleton. The drummer who probably had the
greatest influence on Gene in this period was the great Baby Dodds. Dodds' use of press rolls was highly
reflected in Gene's playing, especially during his tenure with Benny
Goodman.
went to St.
Joseph's College for a brief year. Gene's drive to drum was too strong
and he gave up the idea of becoming a priest. In 1921, while still in
grammar school, Gene joined his first band "The Frivolians." He obtained
the drumming seat as a fluke when the regular drummer was sick. The band
played during summers in Madison, Wisconsin. Upon entering high school
in 1923, Gene became buddies with the "Austin High Gang", which included
many musicians which would be on Gene's first recording session; Jimmy McPartland, Jimmy Lanigan, Bud Freeman and Frank Teschemacher. In 1925, Gene began his
percussion studies with Roy Knapp, Al Silverman & Ed Straight. Under
advice from others, he decided to join the musicians union. "The guy
said, 'Make a roll. That's it. Give us 50 bucks. You're In.'" Krupa
started his first "legit" playing with Joe Kayser, Thelma Terry and the Benson Orchestra among other
commercial bands. A popular hangout for musicians was "The Three
Deuces." All of the guys playing in mickey mouse bands would gravitate
here after hours and jam till early in the morning. Gene was able to
hone and develop his style playing with other jazz players such as Mezz Mezzrow, Tommy Dorsey, Bix Beiderbecke and Benny Goodman in these local
dives. Krupa's big influences during this time were Tubby Hall and Zutty Singleton. The drummer who probably had the
greatest influence on Gene in this period was the great Baby Dodds. Dodds' use of press rolls was highly
reflected in Gene's playing, especially during his tenure with Benny
Goodman.
 With Mal Hallett's Orchestra, 1933
With Mal Hallett's Orchestra, 1933 Krupa played in
one more pit band with Red Nichols for Gershwin's "Girl Crazy." He then
joined Russ Columbo's band in which indirectly led to his
joining Benny Goodman's group. Benny Goodman urged Gene to join his band
with the promise that it would be a real jazz band. After joining, Benny
soon became discouraged with the idea of having a successful jazz group.
The band was relegated to playing dance music and Benny was considering
packing it in. Upon the band's engagement at the Palomar, Benny decided
to go for broke and play their own arrangements. The audience went wild
and the band took off. The Goodman group featured Gene prominently in
the full orchestra and with the groundbreaking Goodman Trio and Quartet.
The Trio is possibly the first working small group which featured black
and white musicians. On January 16, 1938, the band was the first "jazz"
act to play New York's Carnegie Hall. Gene's classic performance on
"Sing Sing Sing" has been heralded as the first extended drum solo in
jazz. After the Carnegie
Hall performance, tension began to surface between Gene and Benny.
Audiences were demanding that Gene be featured in every number and Benny
didn't want to lose the spotlight to a sideman.
Krupa played in
one more pit band with Red Nichols for Gershwin's "Girl Crazy." He then
joined Russ Columbo's band in which indirectly led to his
joining Benny Goodman's group. Benny Goodman urged Gene to join his band
with the promise that it would be a real jazz band. After joining, Benny
soon became discouraged with the idea of having a successful jazz group.
The band was relegated to playing dance music and Benny was considering
packing it in. Upon the band's engagement at the Palomar, Benny decided
to go for broke and play their own arrangements. The audience went wild
and the band took off. The Goodman group featured Gene prominently in
the full orchestra and with the groundbreaking Goodman Trio and Quartet.
The Trio is possibly the first working small group which featured black
and white musicians. On January 16, 1938, the band was the first "jazz"
act to play New York's Carnegie Hall. Gene's classic performance on
"Sing Sing Sing" has been heralded as the first extended drum solo in
jazz. After the Carnegie
Hall performance, tension began to surface between Gene and Benny.
Audiences were demanding that Gene be featured in every number and Benny
didn't want to lose the spotlight to a sideman. Marine Ballroom on the Steel
Pier in Atlantic City during April of 1938. His band went through
several incarnations during it's existance and at one point even
featured a string section with 30 to 40 members. During this time Krupa
authored his own book titled "The Gene Krupa Drum Method"(1938) and
began an annual Drum Contest(1941). The contest attracted thousands of
contestants each year and saw drum legend Louie Bellson as the first
year's winner. Gene appeared in several motion pictures including "Some
Like it Hot" & "Beat the Band", becoming a sort of matinee idol. His
noted likeness to Tyrone Power and musical fame was a magical
combination in the eyes of Hollywood. In the summer of 1943, Krupa was
arrested in San Francisco in a bogus drug bust. He was charged with
possession of marijuana and contributing to the delinquency of a
minor. In truth, the entire incident was a setup by a power-hungry
D.A. Gene was sentenced to 90 days, of which 84 were served. He
was later cleared of the latter charges. During this time, Roy Eldridge led Gene's band and eventually had to
break up the group. After Gene got out of jail, he briefly joined up
with Benny Goodman and Tommy Dorsey before re-forming his own band.
Krupa's groups of the early 1940's were often criticized as being too
commercial but Gene's big band was one of the first in the mid-forties
to introduce Bop arrangements with the help of Gerry Mulligan and the playing of trumpeter Red Rodney. Gene managed to keep the full band
together until December of 1950, when most big bands had already fallen
apart. He kept a smaller version of the big band together through 1951.
Marine Ballroom on the Steel
Pier in Atlantic City during April of 1938. His band went through
several incarnations during it's existance and at one point even
featured a string section with 30 to 40 members. During this time Krupa
authored his own book titled "The Gene Krupa Drum Method"(1938) and
began an annual Drum Contest(1941). The contest attracted thousands of
contestants each year and saw drum legend Louie Bellson as the first
year's winner. Gene appeared in several motion pictures including "Some
Like it Hot" & "Beat the Band", becoming a sort of matinee idol. His
noted likeness to Tyrone Power and musical fame was a magical
combination in the eyes of Hollywood. In the summer of 1943, Krupa was
arrested in San Francisco in a bogus drug bust. He was charged with
possession of marijuana and contributing to the delinquency of a
minor. In truth, the entire incident was a setup by a power-hungry
D.A. Gene was sentenced to 90 days, of which 84 were served. He
was later cleared of the latter charges. During this time, Roy Eldridge led Gene's band and eventually had to
break up the group. After Gene got out of jail, he briefly joined up
with Benny Goodman and Tommy Dorsey before re-forming his own band.
Krupa's groups of the early 1940's were often criticized as being too
commercial but Gene's big band was one of the first in the mid-forties
to introduce Bop arrangements with the help of Gerry Mulligan and the playing of trumpeter Red Rodney. Gene managed to keep the full band
together until December of 1950, when most big bands had already fallen
apart. He kept a smaller version of the big band together through 1951. With Tommy Dorsey & Roy
Eldridge.
With Tommy Dorsey & Roy
Eldridge.

